Startup Funding Stages: Complete Guide from Pre-Seed to IPO
From idea to IPO, Startup Funding Stages define how a business grows, scales, and attracts investors at every milestone. As the global startup ecosystem accelerates and markets like startup accelerators alone are projected to grow from USD 5.02 billion in 2024 to USD 163.3 billion by 2034, founders today face more structured and competitive startup funding journeys than ever before. Each phase of startup funding rounds determines not just how much capital you raise, but when, from whom, and at what cost.
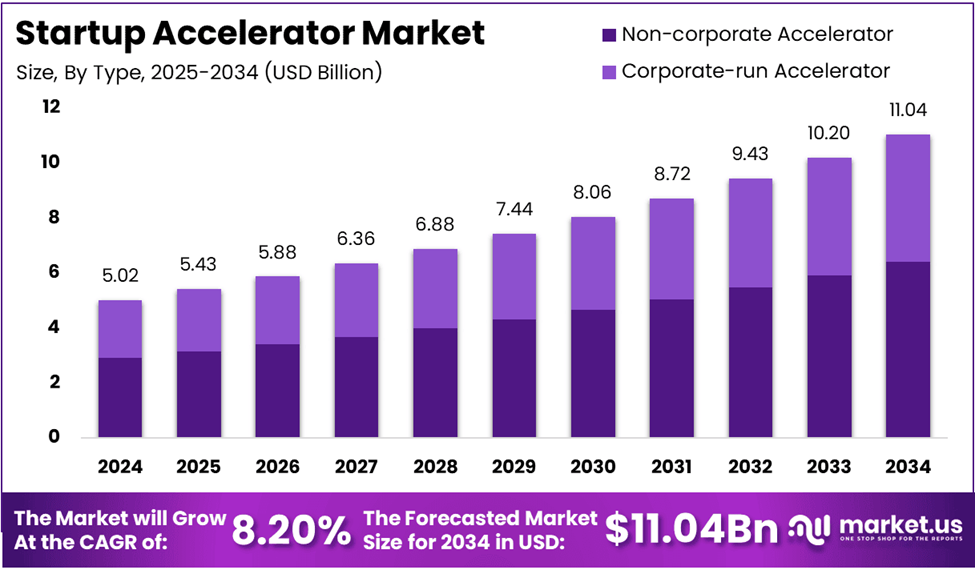
Image Source: market.us
Understanding the process of funding stages for startups will allow the company’s founders to make better decisions, protect their ownership stake, and find the correct set of investors at the appropriate times. This guide articulates the various stages of startup funding from initial market validation to large-scale international expansion, providing clarity on how to navigate through modern-day funding rounds with increased confidence.
How Does Startup Funding Work?
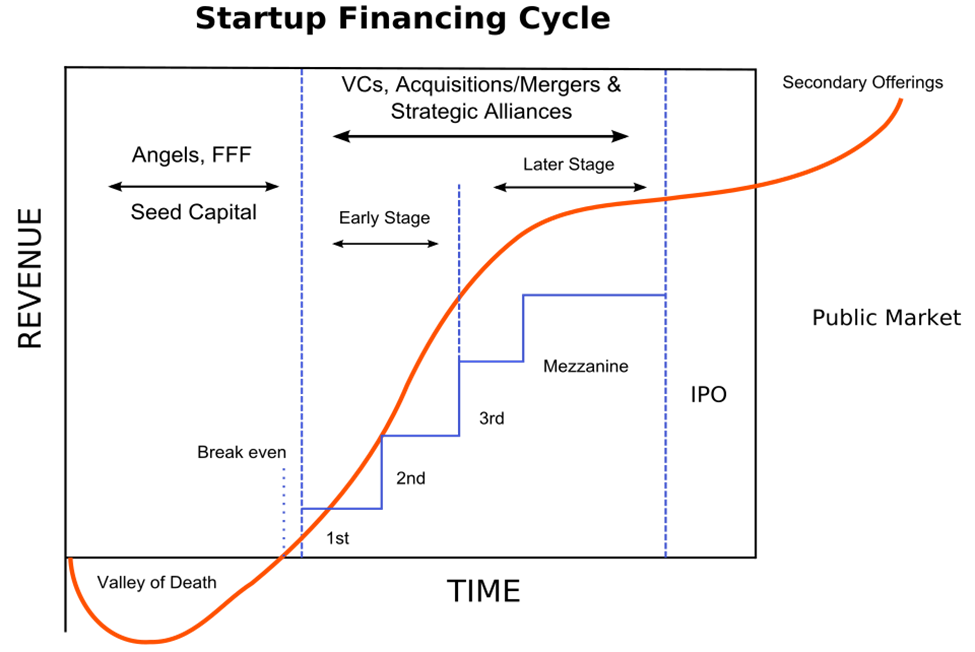
Image source: Wikipedia
At its most fundamental level, the goal of startup funding is to obtain the financial resources required to develop a growing business, by progressing through a startup investment stages that reflect the level of risk and readiness associated with a business’s growth and operational maturity. Think of it as a series of steps up a ladder, with each step representing a different stage of growth, from proving your concept through stages of internationalization and possible public offerings.
Initially, most founders use personal funds, funds raised through family and friends, or funds from angel investors as sources of early stage startup funding in order to create an initial product and to demonstrate that there is an existing market demand for the product. When the product demonstrates promise, funding rounds like Seed or Series A will assist with product and customer development.
The later-stage funding rounds (Series B, Series C, and beyond) typically provide funding through institutional investors to facilitate the rapid expansion of the company.
Stages of a startup funding
The various stages of startup funding refer to the steps that a business takes to acquire money while transitioning through various phases of startup stages (e.g., idea testing, building, launching, financing, and growing). There are distinct phases during which risk drops and the value of a startup increases, and smarter investors begin to pay attention to a startup funding stages, as well as start paying more attention to its future.
To illustrate how these funding stages for startups operate in real terms, by following the progress of one specific startup.
Example startup: FinGrow, a fintech company helping small businesses manage cash flow.
1. Pre-Seed Funding Stage
The Pre-seed funding stage is the earliest of all startup investment stages. At this point, the business is still an idea, with no revenue and often no finalized product.
How it works:
FinGrow’s founders rely on personal savings and small contributions from friends and family. This early startup funding is used to validate the idea, research the market, and build a simple MVP.
Investor focus:
· Founder credibility
· Problem clarity
· Market potential
This stage lays the groundwork for future startup funding stages.
2. Seed Funding Stage
The Seed stage is when the startup starts operating as an actual business. It is one of the most critical startup funding stages, as it determines whether the idea can scale.
How it works:
FinGrow obtains Seed funding from Angel Investors so that the company can officially launch the product, acquire the first customers, and fine-tune the business model.
Investor focus:
· Early traction
· User engagement
· Product-market fit
This phase defines the transition from concept to execution in the stages of startups.
3. Series A Funding
Series A is the first level of significant institutional startup funding round. A company has demonstrated to investors that demand exists and that it will generate revenue.
How it works:
FinGrow raises Series A capital from VCs (venture capitalists), which allows for the expansion of FinGrow’s technology, marketing, and growth strategies.
Investor focus:
· Revenue growth
· Scalable business model
· Clear growth strategy
This is a defining moment in the funding stages of a startup.
4. Series B Funding
Series B funding supports aggressive growth once the business model is validated.
How it works:
FinGrow uses Series B investments from VCs, banks, and other institutions to aggressively pursue additional business growth.
Investor focus:
· Market expansion
· Operational efficiency
· Competitive positioning
At this point, the startup moves firmly into later startup funding stages.
5. Series C Funding
Series C funding helps established startups dominate their industry and scale globally.
How it works:
FinGrow raises Series C to enter international markets, acquire smaller competitors, and invest in infrastructure.
Investor focus:
· Market leadership
· Global scalability
· Long-term growth
This stage reflects advanced startup investment stages.
6. Series D Funding
Series D funding is often strategic and not always required.
How it works:
By raising Series D capital, FinGrow creates a strategic plan for optimizing its financial systems, increasing the company’s perceived value, and preparing for an eventual public offering.
Investor focus:
· Risk management
· Financial stability
· Exit readiness
7. Series E Funding
Series E funding supports final-stage optimization before a major exit.
How it works:
FinGrow invests in brand positioning, enterprise partnerships, and valuation growth.
Investor focus:
· Market credibility
· Sustainable revenue
· Exit timing
8. Series F Funding
Series F funding is used to maximize company value.
How it works:
FinGrow acquires competitors and consolidates market share to strengthen its position ahead of an IPO.
Investor focus:
· Competitive advantage
· Profitability
9. Series G Funding
Series G funding is rare and reflects massive scale.
How it works:
FinGrow raises additional capital to dominate global markets and finalize IPO preparations.
Investor focus:
· Industry leadership
· Global reach
10. IPO (Initial Public Offering)
An IPO is the final milestone in the startup funding stages.
How it works:
FinGrow offers shares to the public, allowing investors to buy stock while early backers exit or partially cash out.
Why it matters:
· Liquidity for investors
· Public market access
· Long-term capital
The most important takeaway here is that by understanding all of the different startup funding stages, the different funding rounds, and overall funding stages for startups, the founder can bring in the correct amount of capital at the appropriate time. As the founder goes through each stages of a startup funding, the eventual goal is for the business to grow sustainably. Solid strategic planning is necessary in all startup stages.
Funding Mistakes Founders Should Avoid
One of the things that is necessary to know before moving on to the startup funding stages is that not all funding is created equally. Each funding stage for startups involves a different type of investor, and therefore, it is important to have investors who will align with your business goals.
Here are a few points to consider seriously before raising the funds:
Funding rounds define control.
Early startup funding may seem small, but equity given away at the seed stage can heavily impact ownership later.
Not every startup needs every stage.
Many successful companies skip certain startup funding rounds or never go beyond Series B.
Timing matters more than valuation.
Raising too early or too late in the stages of a startup funding can slow growth or increase dilution.
Investor fit is as important as capital.
Different startup investment stages attract different investor types, and aligning with your business funding needs is essential.
Understanding these realities will help founders to navigate each startup stage with clarity.
Conclusion: Mastering Startup Funding Stages Sets You Apart
The startup funding stages are not just milestones; they are strategic decisions that shape the future of a business. From pre-seed validation to late-stage expansion and IPO, each phase in the stages of a startup funding comes with unique risks, opportunities, and expectations.
Platforms like Jarvis reach help founders navigate startup funding, connect with the right investors, and align funding strategies with growth goals, making the entire journey smarter and more efficient.
By understanding how startup funding stages work and what investors look for at each level, founders can raise capital more confidently, protect equity, and scale sustainably. Whether you are exploring early stage startup funding or preparing for seed stage startup funding rounds, clarity around the funding stages for startups gives you a competitive edge in today’s fast-moving startup ecosystem.
FAQs
1. Why do most startups fail?
Most startups fail due to poor market fit, running out of cash, or weak execution. Many founders enter startup funding stages without validating demand or managing startup funding wisely, which leads to early burnout and stalled growth.
2. What are the 7 stages of a startup?
The 7 common stages of startups include idea, pre-seed, seed stage startup, Series A, Series B, Series C, and exit or IPO. These startup investment stages help define how businesses grow and progress through different funding stages.
3. Is 1% equity in a startup good?
It depends on the company’s growth potential and valuation. In early startup funding rounds, 1% equity can be valuable if the startup scales successfully through later funding stages for startups or reaches an IPO.
4. What is the 80/20 rule for startups?
The 80/20 rule means 80% of results often come from 20% of efforts. In startup stages, focusing on the most impactful products, customers, or channels can improve efficiency and optimize startup funding stages.







